A quick snippet of the derivation of Einstein’s Mass-energy equivalence equation. This is always good for some good late night reading.
….
In the particle’s rest frame, the momentum is (mc,0) and so for the force four-vector to be orthogonal, its time component must be zero in the rest frame as well, so F = (0,F). Applying a Lorentz transformation to an arbitrary frame, we find
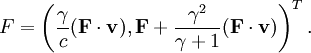
Thus the time component of the relativistic version of Newton’s second law is
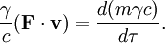
Recalling the definition of work done by the applied force as
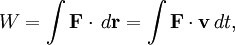
and since the change in energy is given by the work done, we have
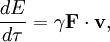
and so finally we see that, up to an additive constant,
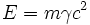
from Wikipedia